Health
Echocardiogram Costs In 2025: A Complete Guide To Pricing, Insurance, And How To Save
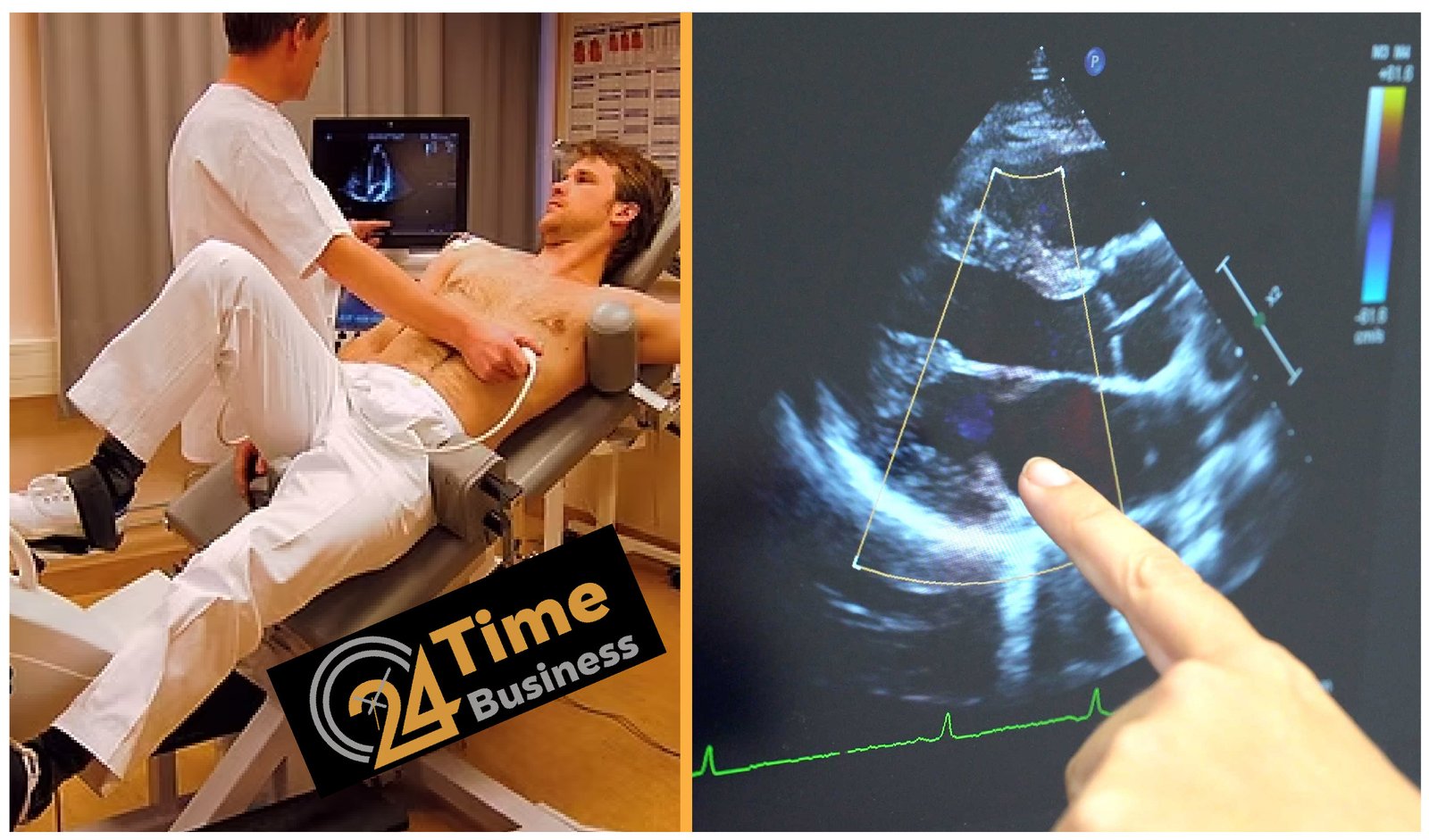
Understanding the echocardiogram cost in 2025 is crucial for patients managing their heart health and budgeting for medical care. An echocardiogram is a non-invasive imaging test that uses ultrasound to assess the structure and function of the heart. While the test plays a vital role in detecting heart conditions, its price can vary significantly depending on location, type, facility, and insurance coverage. Whether you have health insurance or are paying out of pocket, knowing the costs involved helps you make informed and financially sound decisions.
What Is an Echocardiogram?
Definition
An echocardiogram is a diagnostic test that uses high-frequency sound waves (ultrasound) to create moving images of your heart. It is often referred to as a “heart ultrasound.”
How It Works
A transducer device emits sound waves, which bounce off heart structures and are recorded to produce real-time video images. These images help doctors visualize the chambers, valves, and motion of the heart.
Conditions Diagnosed
Echocardiograms are used to detect:
- Heart murmurs
- Valve disorders (like stenosis or regurgitation)
- Heart failure
- Cardiomyopathy
- Congenital heart defects
- Pericardial effusion
Echocardiogram vs. EKG
Unlike an EKG (electrocardiogram) that records electrical activity, an echocardiogram shows the heart’s physical structure and motion. Both are used in cardiac diagnostics but serve different purposes.
Types of Echocardiograms & Their Average Costs in 2025
| Type | Average Cost (Without Insurance) | With Insurance |
|---|---|---|
| Transthoracic Echo (TTE) | $1,200–$2,000 | $150–$500 |
| Transesophageal Echo (TEE) | $2,000–$3,500 | $250–$700 |
| Stress Echo | $1,500–$3,000 | $300–$800 |
| Doppler Add-On | +$300–$800 | +$50–$200 |
| 3D/4D Echocardiogram | $1,500–$3,500 | $300–$900 |
Transthoracic Echocardiogram (TTE)
This is the most common and least expensive type. A transducer is placed on the chest to capture images. No sedation is required.
Transesophageal Echocardiogram (TEE)
A specialized probe is inserted into the esophagus for clearer imaging. This test is more invasive and often used when TTE images are unclear.
Stress Echocardiogram
Performed during exercise or after chemical stimulation to evaluate heart function under stress. Useful for detecting ischemia or blocked arteries.
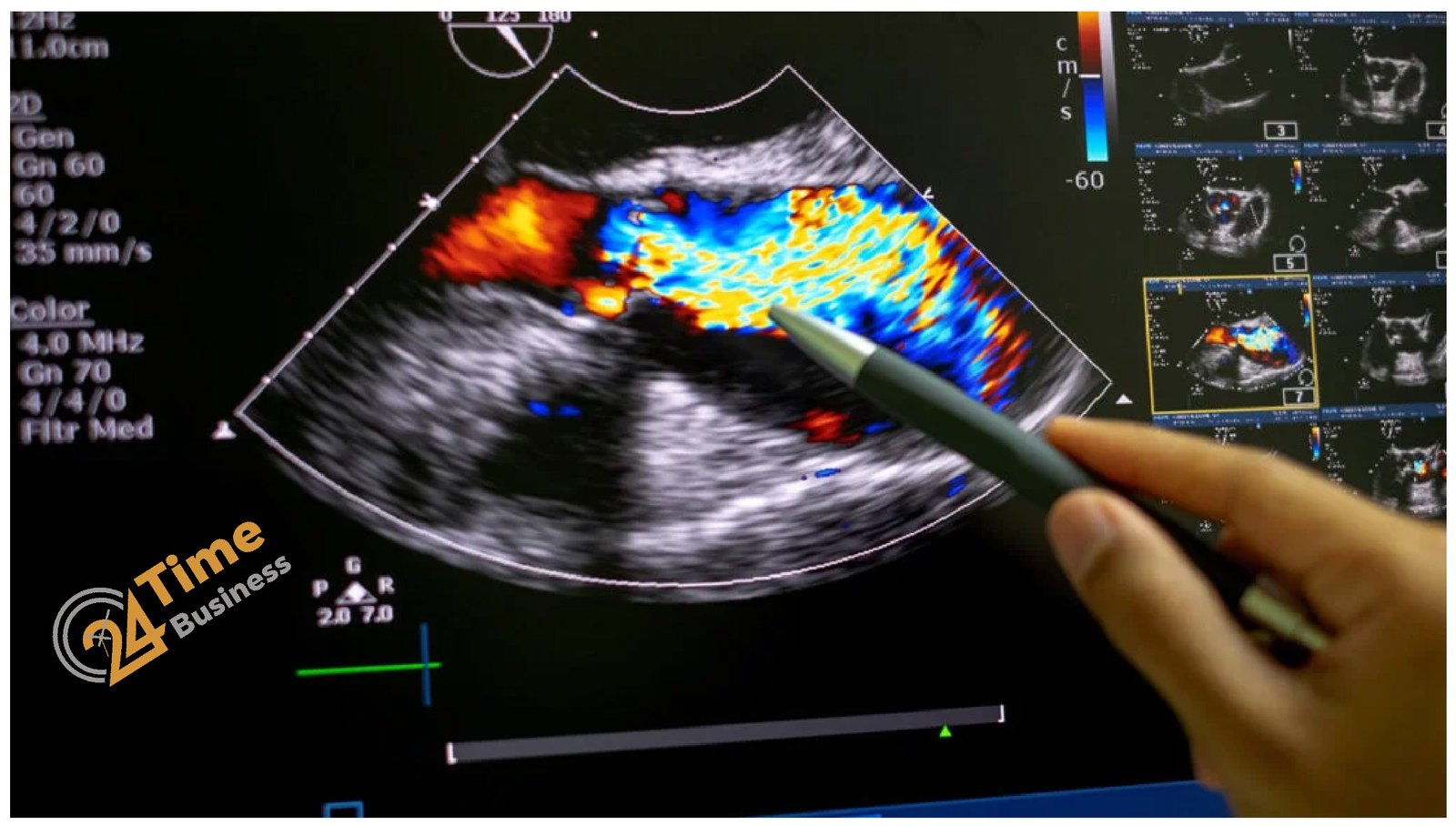
Doppler and Color Doppler
These techniques measure the speed and direction of blood flow. Often used as an add-on to other echocardiogram types to assess valve and blood flow abnormalities.
3D/4D Echocardiograms
Advanced versions of the test providing three-dimensional and real-time imaging. Ideal for surgical planning and complex diagnoses.
Echocardiogram Cost Breakdown: With vs Without Insurance
With Insurance
Costs depend on your insurance plan’s deductible, copay, and coinsurance.
- Medicare: Pays 80% after a deductible (~$257 in 2025); patient pays 20%.
- Medicaid: Varies by state; generally covers medically necessary echocardiograms.
- Private Insurance: Copays range from $50 to $300 depending on the plan.
- High-Deductible Plans: Full cost until deductible is met ($1,000–$2,000 typical).
Without Insurance
Uninsured patients may pay full price:
- TTE: $1,200–$2,000
- TEE: $2,000–$3,500
- Stress Echo: $1,500–$3,000
Always ask about self-pay discounts or financial assistance programs.
Factors That Influence Echocardiogram Cost
Geographic Location
Costs are higher in metropolitan areas compared to rural clinics. For instance, a TTE in New York City may cost $2,000, while the same test in a small town may cost $800.
Facility Type
- Hospital Outpatient Departments: Typically the most expensive due to administrative fees.
- Independent Imaging Centers: Often 30–50% cheaper with similar quality.
- Cardiology Clinics: Mid-range cost but may include comprehensive cardiac care.
Additional Services
- Cardiologist interpretation ($200–$500)
- Sedation (for TEE) can add $100–$300
- Follow-up tests like EKG or blood work
Technology Used
Newer machines with 3D/4D or Doppler capabilities may raise costs but provide more accurate diagnostics.
Urgency of Test
Same-day or emergency tests typically incur higher fees due to expedited services and availability.
Cost Comparison by Provider Type & Location
| Provider Type | Avg. Cost | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Hospital Outpatient | $1,200–$3,500 | Highest cost due to facility fees |
| Independent Imaging Center | $500–$1,800 | Affordable and quicker appointments |
| Cardiology Clinic | $800–$2,500 | Mid-range; includes specialist access |
Medicare and Insurance Coverage for Echocardiograms
Medicare Coverage
- Part A: Covers inpatient echocardiograms
- Part B: Covers outpatient services; 80% coverage post-deductible
- Part C (Medicare Advantage): Covers tests but may require in-network facilities
Medigap
Helps cover deductibles, copays, and coinsurance not paid by original Medicare. Reduces out-of-pocket costs.
Prior Authorization
Required by some private and Medicare Advantage plans. Check with your provider.
Appealing Denials
Patients can appeal denied claims by providing documentation proving the test’s medical necessity.
Echocardiogram Cost Without Insurance
Estimated Costs
- Transthoracic Echo: $1,200–$2,000
- Transesophageal Echo: $2,000–$3,500
- Stress Echo: $1,500–$3,000
Ways to Lower Costs
- Ask about self-pay discounts (10–40% off)
- Consider nonprofit hospitals or university health centers
- Inquire about payment plans or charity care programs
Finding Affordable Facilities
- Use tools like Healthcare Bluebook or MDsave
- Search for local imaging centers with cash price offers
How to Save Money on an Echocardiogram
Use HSA or FSA Funds
Pay with pre-tax dollars to reduce effective cost.
Ask for a Cash Pay Discount
Facilities often offer lower rates for upfront payments.
Compare Provider Prices
Call multiple facilities and ask for self-pay or insured rates.
Check Nonprofit Clinics
Community health centers may provide services at reduced cost or on a sliding scale.
Negotiate Your Bill
Speak to billing departments directly to negotiate pricing or delay payments.
Request an Itemized Estimate
Helps identify avoidable fees or duplicate charges.
When You Might Need an Echocardiogram
- Chest pain or tightness
- Shortness of breath
- Irregular heartbeat
- Persistent fatigue or weakness
- Leg swelling
- Monitoring known heart disease
- Post-heart attack or stroke follow-up
- Pre-surgical evaluation
- Screening for congenital heart defects
What to Expect During the Procedure
Duration
30 to 90 minutes depending on test type.
What Happens
- TTE: Gel applied to chest; transducer used externally
- TEE: Sedation administered; probe inserted through throat
- Stress Echo: Exercise on treadmill or injection of medication
Recovery Time
- TTE and stress tests: Immediate return to normal activity
- TEE: May need short rest due to sedation
Result Interpretation
Images are interpreted by a cardiologist. Results may be available immediately or within a few days.
Alternatives to Echocardiogram (and Their Costs)
ECG / EKG
- Measures heart rhythm
- $100–$300
Cardiac MRI
- Detailed heart imaging
- $1,500–$4,000
CT Angiogram
- Visualizes coronary arteries
- $1,000–$2,500
Each alternative serves different purposes and may complement or replace an echo depending on clinical needs.
Conclusion
Echocardiograms remain a vital tool for detecting heart conditions in 2025. While the cost can range from a few hundred to several thousand dollars, understanding your options—from insurance coverage to alternative providers—can significantly reduce your financial burden. Be proactive: verify benefits, ask questions, compare prices, and explore available assistance programs. Your heart health is too important to neglect due to uncertainty around costs.
FAQs About Echocardiogram Cost
1. How much does an echocardiogram cost without insurance?
The cost of an echocardiogram without insurance can range from $1,200 to $5,000 depending on the type of test (e.g., transthoracic, transesophageal, or stress echocardiogram) and location.
2. Does Medicare cover echocardiograms?
Yes, Medicare covers echocardiograms when deemed medically necessary. Part A covers inpatient tests, while Part B covers outpatient tests, with patients typically responsible for 20% of the cost after meeting the deductible.
3. What is the average out-of-pocket cost for an echocardiogram with insurance?
With insurance, the out-of-pocket cost for an echocardiogram typically ranges from $150 to $500, depending on your insurance plan, copay, and deductible.
4. What factors affect the cost of an echocardiogram?
Several factors influence the cost of an echocardiogram, including the type of test, location (urban vs. rural), facility type (hospital vs. independent clinic), and whether additional services (like a cardiologist’s interpretation) are required.
5. How can I reduce the cost of an echocardiogram?
To reduce costs, you can ask for self-pay discounts, compare prices from multiple providers, and use HSA/FSA funds. Some facilities may also offer payment plans or financial assistance programs.
People See More: What Is The Kellogg Innovation Network? A Complete Guide To KIN, TWIN & The Future of Innovation

-

 Celebrity2 months ago
Celebrity2 months agoWho Is Dora Zbierlund? The Untold Story of Jeffrey Tambor’s Ex-Wife and 1980s TV Actress
-

 Biography2 months ago
Biography2 months agoWho Is Jonathan Tham? The Two Doctors Making A Difference Beyond Fame
-

 Celebrity2 months ago
Celebrity2 months agoDounne Alexander: The Inspiring Herbalist Who Transformed Britain’s Natural Health Movement
-

 Celebrity2 months ago
Celebrity2 months agoGuy Willison Biography (2025): Age, Wife, Illness Update, Net Worth & Motorcycle Legacy















